Catharanthus roseus / Rose periwinkle / নয়নতারা

General features: It is a perennial flowering plant commonly known as Rose periwinkle / Madagascar periwinkle which is botanically titled as Catharanthus roseus. The plant belongs to Apocynaceae / ‘dogbane’ family, grown mainly in the warm tropical climate, often claimed to be the native of Madagascar but grows wildly in the tropics of South Asian nations like India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Thailand, and Indochina including Australia, Spain, USA and parts of mainland China. In Bengali, it is named ‘Nayantara’ (নয়নতারা) meaning ‘eyeball’. Although regarded to be ornamental but the plant earns incredible reputation for its immense medicinal values, particularly being the original source of several multi drug resistance potent anticancer drugs, Vincristine and Vinblastine and equivalent others, also considered to be the large source of Vinca alkaloids having enormous medicinal role. The evergreen shrub / subshrub grows ~ 3.5 feet tall displaying oblong shaped 1.0 – 3.5 inches long and 0.5 – 1.5 inches wide glossy green leaves with short petioles (0.5 – 0.8 inch) which are arranged opposite pairs. The flowers have mixed range of white to pink color with darker pink or red coloration at center. The basal tube is 1-1.5 inches long and the corollas are 1 – 2.0 inches having five petal lobes. The fruits are follicles ~ 1.5 inches long and ~ 0.5 in wide. The plant is now considered as an endangered species.
History and Folk medicinal use: The plant was at first named Vinca rosea by the famed Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus around 1750 which was later renamed as Catharanthus roseus in 1834. In 1922, the US pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly started to extract this plant in an attempt to find its versatile medicinal ingredients basing on the folk use. In 1958, its anticancer potential was scientifically detected. Besides Eli Lilly, the university researchers from Ontario, Canada also identified the similar effects, killing leukemic white cells in vitro. The attempt to cure Leukemia was initiated at first which afterward led to identify the active anticancer ingredient, Vincristine an alkaloid offering potent anticancer role. It took ~ 900 Kg of dried leaves to produce 1.0 gm of Vincristine. The drug has been approved by FDA in the US for Leukemia and Hodgkin lymphoma therapy around 1961. Besides the well-publicized anticancer therapy, the plant extract is used to treat a large number of diseases: Bacterial infections, Acne, Allergy, Abscesses, Viral infections, Diabetes, High blood pressure, Diarrhea, Malaria, Conjunctivitis, menstrual irregularities and many others. Considering the cancer therapy, besides Leukemia or Hodgkin Lymphoma, the extract shows decent success in treating the Lung cancer, Colon cancer, cervical cancer, Breast cancer, anal cancer, Liver cancer, malignant lymphoma, neuroblastoma, Wilms’ tumor and rhabdomyosarcoma. The alkaloids or plant extract shows number of side effects eg, alopecia, nausea and bone marrow suppression. Europeans used this plant to remove headache and controlling of diabetes which has been noticed also in many South Asian nations like Malaysia and Indochina. It also shows antispasmodic and antihypertensive effects. The plant extract indicates memory enhancing property along with its vasodilating effect. It alleviates vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disorder. Smoking dry leaves may cause hallucination and lack of coordination. The frequent use of C roseus extract may cause kidney and nerve disorders. As per Ayurvedic medicinal consideration, decoction prepared from stem, roots and leaves are used to treat hypertension, gastro-intestinal problems, diabetes and menstrual disorders and other female sexual problems.
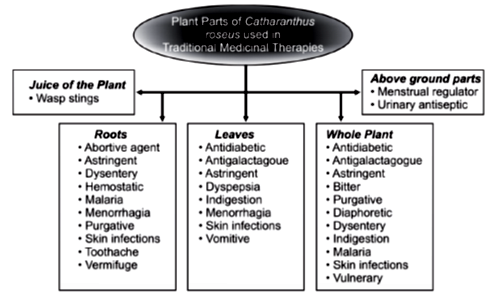
Use of C. roseus uses in different countries for various purposes.
| Country | Use |
| India | Leaf extract is used to treat bee or wasp sting. |
| Philippines | Leaf extract is used to control diabetes, stomach cramp, menorrhagia, cancers
Root extract is used against intestinal parasite, cancers and dysentry. |
| Madagascar | Leaf extract is used as vomitive. Roots used for purgative, depurative, vermifuge, toothache. |
| Mauritius | The juice from leaves is used for indigestion and dyspepsia. |
| West Indies
& Nigeria
|
Used for controlling diabetes. |
| Cuba &
Jamaica |
Extract of flower is used for eye wash during infection. |
| Bahamas | Decoction from flowers is used to control asthma, tuberculosis and flatulence. |
| Malaysia | Plant extract is used to control diabetes, hypertension, insomnia and cancer. |
| America | Gargling with extract lessens soar-throat, laryngitis and chest ailment. |
| Africa | Leaf extract is used for menorrhagia and rheumatic problems. |
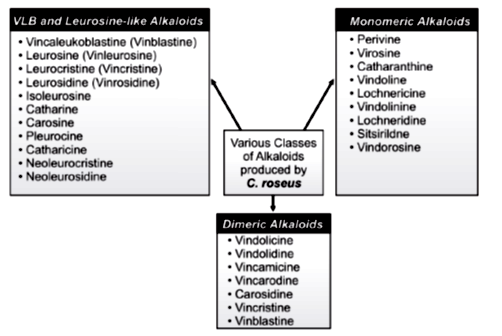
Chemical components and medicinal effects: The plant possesses carbohydrate, flavonoids, saponins, essential oils and alkaloids. It also produces appreciable quantity of essential oils. The major ingredients within the oil is: Leaf oil contains – Linolenic acid ethyl ester (~44 %), Stearic acid (~11 %), Phytol (~ 7%), Hexadecanoic acid (~7%) whereas the oil from flower contains – Limonene (~34%), phytol (~30%) and Linolenic acid ethyl ester (~14%). Among all the known components of C. roseus, alkaloids produce significant impact for their potent anticancer role to cure or control large categories of cancers. The plant synthesizes large number of various (~ 400) alkaloids of which a significant number are used for the sake of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, fragrance, flavor, food additives and pesticides. Most of the alkaloids of this plant belong to terpene-indole family, often abbreviated as TIA, Terpenoid Indole alkaloid. These are distributed both in aerial parts and roots in versatile ways.
Distribution of various alkaloids in plant
| Plant parts | Alkaloids |
| Plant | Tabersonine, Voafrine, Vindolinine-N-oxide, Vinecaleukoblastine, Ajmalicine,
Calmodulin, Isovincoside, Leucristine, Leurosine, Reserpine, Serpentine, Vindoline. |
| Leaf | Vinecaleukoblastine, Vindolinine-N-oxide, Vindolinine, Leurosine,
Deoxy- Vinecaleukoblastine, Vincoline, Zeatin. |
| Flower | Catharicine, Indole-3-acetic acid, Hirsutidin, Malvidin, Vindolicine, Zeatin. |
| Root |
Ajmalicine, Alsotonine, Carsodine, Leurosivine, Vincaline, Vinsodine, Virosine, Zeatin. |
They are synthesized through the secondary metabolic pathways following medium alkalinization, Ca+2 influx, receptor mediated signaling and oxidative bursts. Their production has been enhanced by the transcription of respective related genes. Further, UV-B causes dimerization of TIA acting as abiotic elicitor. In general, TIA protects against microbial infection and abiotic environmental stresses eg, UV radiation.
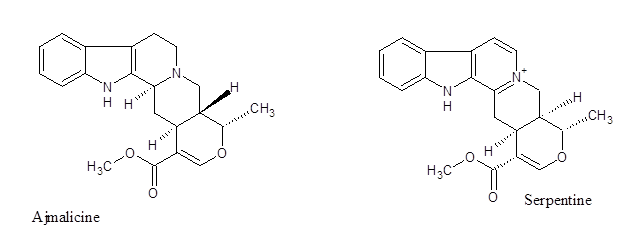
The monomeric alkaloids Ajmalicine and Serpentine exert anti-hypertensive effect. Ajmalicine acts as α1 – adrenergic antagonist with partial recognition to the α2 – adrenergic receptor imposing anti-hypotensive effect. Serpentine mediates antipsychotic action by interacting with 5-HT2A/C receptor. It also exhibits good anti-oxidant effect and inhibits nuclear translocation of NF – κβ.
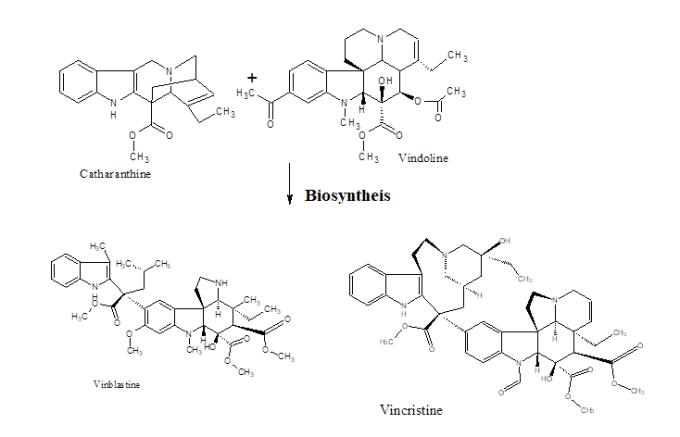
The anti-tumor dimeric alkaloids eg, Vincristine and Vinblastine are biosynthesized in the leaves by conjugating with Catharanthine and Vindoline.
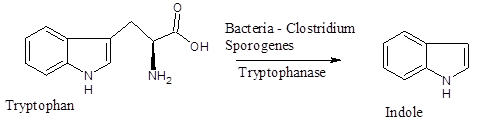
The indole alkaloids bear the structure of indole moiety. It is one of the largest classes of alkaloids known so far. About 4100 of them are identified having considerable physiological actions that are often used in different medicines. All are biosynthesized in the plant using the amino acid Tryptophan as their main precursor by using the enzyme tryptophanase or by the intestinal bacteria, Clostridium sporogenes that also produces that enzyme for breaking down the tryptophan. The medicinal properties of many of the alkaloids are known from the time of ancient civilization in India or Aztecs in South America around 1000 BC. The discovery of Indole in 1866 by chemically decomposing the dye, Indigo from plant by Adolf Von Baeyer, a German scientist further initiated the search to find other related compounds.
In C. roseus, the Vinca alkaloids are synthesized in the stem as milky sap which is poisonous by nature. About 0.86% of the alkaloids are located in the root whereas ~ 0.67% in leaves and ~ 0.37% in the stem. Those alkaloids can arrest the proliferation of several cancer cells by binding to the tubulin in mitotic spindle. It also induces apoptosis thereby suppresses the spreading of cancers. Most of the alkaloids from Vinca family are high valued compounds for its immense therapeutic role especially in the treatment of numerous cancers eg, breast, ovary, lung, colon, rectum, testis, leukemia, Hodgkin’s diseases and neuroblastoma. The compounds are integral part of chemotherapy regimen. Normally, they are administered intravenously. These are effective against multi-drug resistance tumors or cancers. A few important ones are discussed below.
Vinblastine –
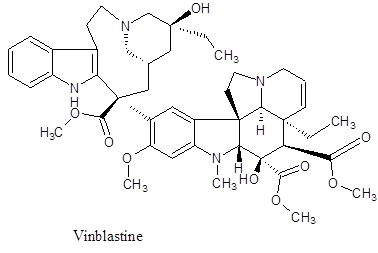
The compound is available in sulfate form as white crystalline, water soluble and moderately hygroscopic by nature. Physiologically, it exerts anti-mitotic effect thus widely used to control number of cancers like, breast, non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck cancers, testicular cancers and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It quite resembles to Vincristine. The drug binds to tubulin and subsequently inhibits the assembly of microtubules thereby preventing the cell cycle particularly at its M phase. The alkaloid can raise the five year survival rate to almost 98%. It combats cancer by interfering with glutamic acid metabolism. It is also useful in treating Kaposi’s sarcoma and breast carcinoma as well. It is very toxic and suppresses bone marrow inducing gastrointestinal toxicity a potent vesicant, causing blisters or extravasation injury and embryo-toxic therefore not prescribed during pregnancy. Breast feeding is barred during treatment with Vinblastine since it is noticed to secrete in the breast milk. Patients having any infections are not prescribed for it.
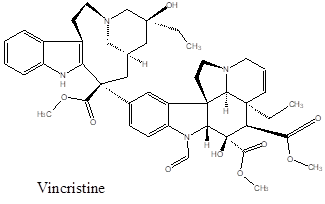
It is also a mitotic inhibitor, largely used for cancer chemotherapy naming as Oncovin and approved by the FDA in 1963. The compound binds to tubulin dimer thus inhibits the assembly of micro-tubule structure preventing mitosis in metaphase state during the cell cycle. It affects all rapidly dividing cells which particularly includes the cancers but also intestinal epithelial and bone marrow cells. It is delivered intravenously to the patients. Vincristine is often used along with drug regimen like, Doxorubicin, Adriamycin, Cyclophosphamide and Prednisone. Both Vinblastine and Vincristine are employed in sub-micromolar range from 10 nM to 1.0 µM. In a strange way, over 10 µM concentrations it causes tubulin aggregation rather than disruption. The regimen are frequently administered in the case of acute lymphoblastic leukemia also for the Wilms’ tumor and nephroblastoma. The compound is highly toxic may cause peripheral neuropathy, constipation, hyponatremia and hair loss. The intrathecal administration often causes massive encephalopathy, demyelination of spinal neuron inflicting severe pain which can cause fatality. Occasional lung spasm causing breathing problem might also develop. The use of Vincristine or Vinblastine also induces thrombopenia, leucopenia, motor weakness, psychosis, convulsions, neuropathy and peripheral neuritis. Despite its various adversarial effect, it is still a very effective ingredient in cancer treatment.
Vindesine –
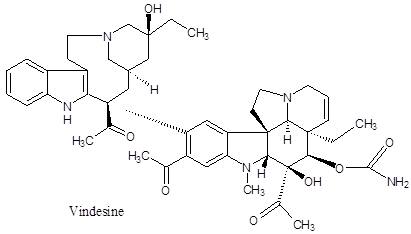
It is also an anti-mitotic alkaloid soluble in water, often used in the chemotherapy for cancers of Leukemia, Lymphoma, melanoma, breast, lung and uterine cancers. Its side effects are almost to others.
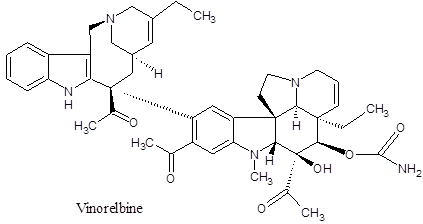
It is also an anti-mitotic agent and effective against non-small cell lung and breast cancer. It is also used for other tumor and cancer therapies and possesses less side effects especially on the nervous system. It reduces immunity toward infections causes anemia, diarrhea, hyponatremia, numbness and tingling of hands and feet.
Other therapeutic properties: The extract from plant, leaves, flowers and roots provide numerous health benefits in addition to its powerful anti-tumor actions: A) it can lowers blood glucose level to 50 – 60% due to increased glucose utilization in the liver; B) It has strong anti-microbial actions against Salmonella typhimurium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa; C) Powerful anti-oxidant especially Vindolicine; D) antihelminthic that protects human and cattle; E) Hypotensive, sedative and tranquilizing effect; F) Anti-diarrheal action; G) Hypolipidemic effect, lowering Cholesterol, LDL and VLDL. Below is the diagram for various use of different parts of C. roseus extract.