Cassia sophera / Sena sophera / কলকাসুন্দি

General features: The shrub is commonly known by the name Sena sophera. Its English name is Cassia sophera (C sophera). In India, it is called Kasundi in Hindi whereas in Bengali, its name is given Kolkasundi (কলকাসুন্দি). It is a tropical plant that normally grows in the wastelands or forests. It is a genus of Cassia Linn and belonging to Fabaceae family (Caesalpiniaceae subfamily). There are about 600 species widely distributed all over India and other tropical regions of the world. It is presumably originated from India / Bangladesh or other South East Asian countries and in some places of Southern China. Besides the Asian nations, it is also found in several South American and African countries. The shrub is used as a folk medicine in rural areas mostly for treating respiratory ailments. It is a good source of mucilage, flavonoids, polysaccharides and Anthraquinones. Phytochemical identification indicates that it provides high level of antioxidants. Although considered being a medicinal plant but frequently used for edible purposes as a vegetable green particularly the leaves or green pods cooked with spices. Normally, the fresh pods are used to make curry. Whereas the dried seeds and leaves are occasionally used as substitute for coffee. The plant reaches to a height of ~ 10 ft. The leaves show insect repellant property. It is often allowed grow along with the other crops. This practice prevents damages from the land snails. Due to insecticidal action, dried leaves are stored with stockpiles of grains. The plant has ability of fixing nitrogen in the soil. It is also used for the ornamental purposes for bright yellow flowers which are racemes by nature. The leaves or leaflets have tapering at the end with single gland at the base. In recent days, the use of various members of Cassia are rising. C sophera is particularly one of them. The plant possesses enormous medicinal potential while acting as anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-parasite, anti-inflammatory, and anti-diabetic and other beneficial role. Due to its large reserve of anthraqunone derivatives it also acts as good laxative.
Folk / traditional medicinal uses: The leaves are mostly utilized for traditional folk medicine that contains high level of Kaempferol and Anthraquinone derivatives (Chrysophanol, Physcion, Rhein, Emodin and others). Those components are known to have anthelmintic, expectorant and febrifuge effects. The infusion prepared from leaves can control or cure rheumatism, fever, inflammation and malaria. The leaf extract is able to cure conjunctivitis also helps healing wounds and cure ringworm infection. The extract also shows anthelmintic property. The decoction made of roots or barks helps relieving painful menstruation also, if given to children can stimulate the nervous system. The bark extract can efficiently control diabetes. The extract of entire plant can restrain epilepsy. The seeds reduce fevers also treat nephritis or Bright’s disease. According to the Unani medicine, also mentioned in ethno-pharmacological literature, the herb is highly effective in treating Pityriasis, Psoriasis, Asthma, acute Bronchitis, Cough, Diabetes and convulsions among the children. It is also effective in controlling osteoarthritis.
Chemical components: The major phyto-chemicals in C sophera are alkaloids belonging to Piperidine family, flavonoids (rutin, rhamnetin, kaempferol and quercetin), Anthraquinones and essential oils which have numerous terpenes and long chain fatty acids. Advantageously, the essential oil extract from C sophera is used for preserving food and beverages because of the antimicrobial constituents. Usually, essential oils are counted to be non-toxic but active against numerous micro-organisms although the limit to be added should be judiciously considered since it may create adverse reactions like nausea, vomiting or irritability on skin. But majority of Cassia species have noticeably large content of Anthraquinone derivatives either in free or with glycosidic linkage.
Naturally occurring Anthraquinone derivatives in Cassia sophera
Anthraquinones are the organic molecules having 9, 10 di-oxo-anthracene moiety. Until now, about 79 naturally synthesized anthraquinone derivatives are identified. Among them the notable ones are Emodin, Physcion, Rhein, Chrysophanol and Sopheranin and few others. They have been known widely for bioactivities while working as anticancer, anti-inflammatory, diuretic, anti-diabetic, vaso-relaxing and exhibiting phyto-estrogen actions. They are seen particularly effective against tumor proliferation and auto-immune disorders. In that way, many of the anthraquinone derivatives help prevent from life threatening metabolic problems.
Interestingly, replacing any of the side groups by – OH, the molecule(s) is often referred as hydroxy anthraquinone(s) which displays the bright color by absorbing light at the visible range of wave length. Usually, anthraquinone derivatives have their characteristic absorption spectra. The existence of typical chromophore like conjugated double bonds produces strong absorption at the UV region. The UV absorption majorly occurs due to benzenoid transitions in addition to the absorption by the quinonoid groups displaying peaks around 240 – 260 nm having the high intensity at 250 nm also around 320 – 330 nm with medium sized peak, further especially at 322 nm. The quinonoid band appears at 260 – 290 nm. Those characteristic band patterns are not tremendously affected by the substitution on phenol rings. The unsubstituted anthraquinone has small peak at 405 nm thereby displaying light yellow color. The substitution at 1 and 4 positions causes strong bathochromic shift intensifying colors more than any other substitution. Usually, the colors of naturally occurring anthraquinone derivatives vary from light yellow to dark red, brown and pink or violet. Owing to its quinonoid moiety, anthraquinones can efficiently take part in the redox reactions exerting both anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant reactions. Emodin and Physcion acts as anti-oxidant causing anti-microbial effect. As per the exception, only a few expresses pro-oxidant behavior. For example, Chrysophanol accelerates peroxidation of Linoleic acid. Chemically, anthrone, anthraquinones and substituted anthraquinones particularly with phenolic –OH at C1, C6 and C8 and even with methylated (-CH3) group at the C3 position act as anti-oxidant displaying significant scavenging of generated free radicals. The order of anti-oxidant activity is, Anthrone (95 %) > Alizarin (93 %) > Aloe-emodin (78 %) > Rhein (71 %) > Emodin (36 %) > Anthraquinone (8%). Experiments convinced that the anti-oxidant behavior of these derivatives are mostly due to the scavenging effect of free radicals also including the innate reducing ability. On the contrary, the pro-oxidant effect of Chrysophanol is exerted by enhancing the free radical production. Further it has been also established that these derivatives act as good metal chelating agents. They can efficiently chelate the toxic metal ions like, Cu+2, Al+3, Hg+2 and Cd+2 or others of similar category. The chelation of mercury by natural anthraquinones produce non-toxic complex thereby relieving the intracellular – SH group(s) free to work accordingly. Most of the anthraquinone derivatives show anti-tumor activity due to the cytotoxic effect on those cells. In frequent occasions, they are able to control multi-drug resistance cancer cells by inducing apoptosis following different intracellular pathways as seen in case if breast adenocarcinoma, MCF-7 while arresting the cell cycle at G1 phase. Experiments show that numerous cancer / tumor cells stop proliferation when exposed to different naturally occurring anthraquinone derivatives. Emodin can suppress cervical cancer by blocking neo-vascularization and promoting the apoptosis. Emodin also inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer cell line, PANC-1 by demethylating the tumor suppressor gene. Although Emodin shows many of its anti-cancer properties but FDA has not approved it for treatment since it is also a potential carcinogenetic substance. Further it causes diarrhea, nausea and renal failure. It has been noticed that even majority anthraquinones have great potential as anti-cancer drugs controlling versatile categories of cancers but its application is also a major concern so it should be administered very judiciously.
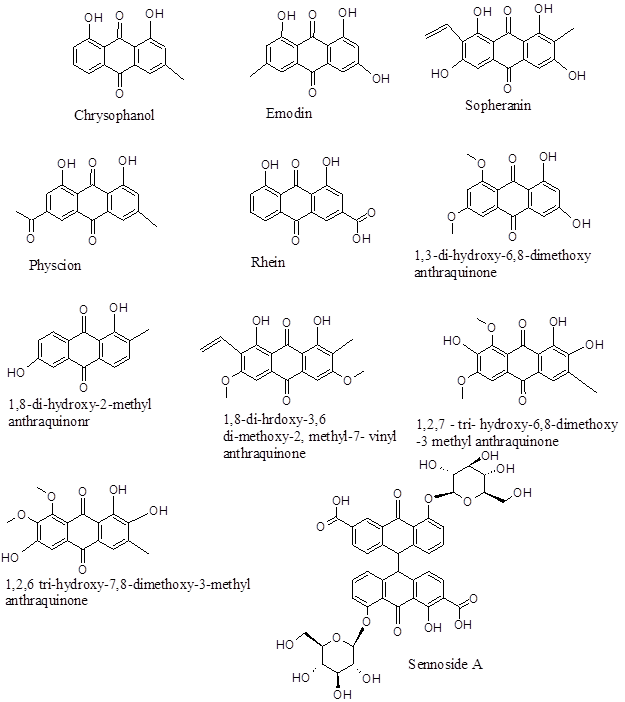
Major anthraquinone products in C sophera
Regarding anthraqunone content, the derivatives are synthesized slight differently in parts of the plant. Leaves and flowers have most of the Sennoside isomers and Chrysophanol whereas the roots and barks have 1,8-dihydroxy-2-methyl-anthraquinone, Chrysophanol, Physcion,1,8-dihdroxy-3,6-3,6-dimethoxy-2-methyl-7-vinyl-anthraquinone, 1,3-dihydroxy-5,7,8-trimethoxy-2 methyl-anthraqunone and heartwood has 1,2,7-trihydoxy-6,8-dimethoxy-3-methyl anthraqunone, 1,2,6-trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-3-methyl Anthraquinone, Chrysophanol, Physcion, Emodin and Sopheranin.
Flavonoids in C sophera
The plant has appreciable amount of flavonoids. Among them, the majorly found ones are, Quercitin, Rhamnetin, Kaempferol and Rutin. The beneficial effect of them are widely known. The flavonoids are poorly absorbed in the human body (~ 5 %). It is also quickly metabolized and excreted. So it has been presumed that the anti-oxidant effect in blood is mostly due to the production of Uric acid but less from the absorbed intact flavonoids. The further physiologic effect is provided by its scavenging action on generated free radicals. Adding those together, it is quite evident that flavonoids are overall beneficial to health while acting as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-bacterial as well lowering the risks from cardio-vascular diseases. Besides the flavonoids, there are also appreciable amount of tannins present in the plant. Flavonoids are widely for its beneficial role in health especially acting as good anti-oxidant. In general, they act as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic and simultaneously lower the cardio-vascular risks by lowering the cholesterol and lipids in circulating plasma.

Major flavonoids in C sophera
Piperidine alkaloids
Most of the Cassia species synthesize several Piperidine alkaloids which is noticed also in C sophera also. Piperidine moiety is the characteristic of this alkaloid. About 700 of them are identified in both plant and animal kingdoms. Some of them possess high level of toxicity. They are widely known for anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, anti-histaminic, herbicidal, fungicidal and insecticidal properties. In addition they have potent actions on central nervous system while acting as stimulant as well as depressant also impose actions by interacting with the nicotinic receptors within neuromuscular joints.

Essential oil
The leaves of C sophera is the major source of essential oil (~ 0.8 % w / w). Approximately 29 components have been identified having 94.1 % oil composition. The major ones are Benzyl alcohol (9.1 %), Iso-eugenol (5 %), Germacrene D (4.8 %), Iso-creosol (5.7 %), Phenyl ethyl alcohol (5.1 %), Azulene (4.7 %) and Linolenic acid (1.6 %). Benzyl alcohol acts bacteriostatic, preservative and used against removing head lice. Iso-eugenol exists in cis – and trans – isomers. Both of them find uses in cosmetics. Germacrene D is a sesquiterpene which shows antimicrobial and insecticidal properties. It plays the role of insect pheromone. Iso-cresol has strong antimicrobial effect. Phenyl ethyl alcohol has the pleasant odor which is produced by the fungus named Candida albicans exerting anti-microbial and preservative effects. Azulene is a pigment displaying the blue color and often used in the cosmetics. Linolenic acid is a ploy-unsaturated fatty acid exists in ci s– and trans – forms having several isomers showing olefinic bonds at different positions creating α – (ω -3 or n – 3 fatty acid) and γ – (ω – 6 or n – 6 fatty acid) isomers. They are actually dietary components having distinctive beneficial role on health. The large variety of individuals show anti-bacterial and anti-microbial effect. In that context, the use of essential oil as a whole is noticed to have the potent anti-bacterial effect also for human pathogenic and bacteria from the soil. The extracts by any solvent either hexane, ethyl acetate or alcohol show almost the similar anti-bacterial behavior with slight variations.
Pharmacological actions of C sophera: The plant has large potential for medicinal actions. In that regard its pharmacological effects needs to be highlighted since several activities may not be beneficial for health. Following is the discussion about some of the important pharmacological effects.
Analgesic effect – The seed extract of C sophera induces analgesia centrally as indicated by the laboratory experiments using external thermal nociceptive stimuli confirming the opioid type analgesic effect. The inhibitory effect of flavonoids on pain perception has been well documented which occurs due to the prevention of generation of inflammatory mediators. It has been further recorded that flavonoids can enhance the serotonin level which in turn interacts with the receptors 5-HT2A and 5-HT3 producing analgesic action centrally. In a way, both anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions are credited for those flavonoids present in seed.
Anti-oxidant effect – In vitro experiments indicate that the constituents present in the extract of C sophera have strong free radical scavenging ability. The identifiable components are mostly flavonoids or glycosides.
Hepato-protective effect – Applying experimental animal model while inducing hepatic damage using CCl4, it has been reported that ethanolic extract of C sophera leaves can efficiently prevent the injury. The fact has been verified biochemically and histo-pathologically. The leaf extract can bring back the level of AST, ALT and ALP and total bilirubin content to normal. The identifiable constituents are flavonoids.
Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic effect – The aqueous extract of C sophera leaves exhibits potent hypoglycemic effect by enhancing the peripheral glucose level within Streptozotocin induced diabetic laboratory animals. It also significantly lowers the elevated level of Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) ~ 50 % with simultaneous increase of insulin level (~ 41 %). The level of total cholesterol (~20 %), LDL (~ 22 %) and triglycerides (~ 58 %) in circulating also decline considerably. The further investigation indicates that the leaf extract has strong stimulating influence on pancreatic β – cells to release insulin and the effect is not mediated by the K-ATP channel. Although no definite compounds are identified but the suspected agents might be the combination of alkaloids and flavonoids.
Anti-inflammatory effect – The ethanolic extract of leaf shows significant anti-inflammatory action when tested on the laboratory animals. The level of PGE2, PGF2 Serotonin and histamine are seen to be alleviated including the peptide Substance P. The identifiable components are flavonoids and saponins. Among them Rhamnetin is noticed to be the predominant factor.
Anti-asthmatic effect – The extract of C sophera shows potent anti-asthmatic behavior due to its anti-allergic, anti-histaminic and anti-inflammatory as well as adaptogenic properties. It also works as an effective bronchodilator while preventing or controlling the asthma attack.
Anti-bacterial effect – The ethanolic extract of C sophera leaves can efficiently control the growth of numerous pathogenic bacteria from the soil. The identifiable components are within the mixture of essential oils which contains ~ 29 components.
Laxative effect – The strong laxative effect of C sophera has been noted for a long time. The identified compounds are anthraquinone alkaloids along the mucilages built in the plant.
