Boerhavia Diffusa / Red spiderling / Punarnava / পুনার্নভ ।

General features: It is a flowering plant of ‘four o’clock family’ (Nyctaginaceae). Besides holding the name Boerhavia diffusa (BD), the plant is also called ‘Red spiderling’ in English. In India, BD is commonly known as Punarnava (পুনার্নভ) meaning ability to rejuvenate the body and soul as suggested by the reputed ancient Indian apothecary, Ayurveda. It is a plant with diffuse inflorescences. The inflorescence occurs at end of each branches and forked about 3 – 6 times. The branches are divergent ending with 2 – 5 flower clusters. The leaves are ~ 0.4 inch long simple opposite, short petioled, ovate-oblong, acute or obtuse, subcordate base glabrous above. Flowers are small pale rose in color. Fruits are highly viscid, easily detachable and one seeded. The bract at flower base is lancelike ~ 0.3 – 0.4 inch. The name ‘four o’ clock’ is derived for the flowers since they open in the afternoon and close at morning. It is this natural behavior that provide the name. The flowers grow with white, yellowish shades, pink to red or even spotted with other shades. The plant belong to Boerhavia genus. It has approximately 45 species belonging to this class. One of the species among them is Boerhavia diffusa which grows small red flowers with a touch of pleasant smell. In India and in many places of South East Asia BD is used as vegetable green. Additionally, it is often used as a pain medication. The plant grows mainly in tropical and subtropical climates like in India, Pacific island nations, Caribbean islands, South Asian nations, Latino countries and Southern parts of US. It is often characterized as weed. It is a perennial herb with stout root stock holding multiple branches. The herb is widely reputed mainly for its antiinflammatory and analgesic actions. In tribal inherited places of India, the roots are routinely used to treat various hepatic disorders and internal inflammations. In recent days, it is seen effective in treating edema, ascites and early stages of liver cirrhosis and peritonitis as well. Usually the whole plant or its roots or their extracts are used for treating several serious ailments. Although frequently used as vegetable in many places, the plant contains slight bitter or astringent taste.
Medicinal properties and uses: The extracts of whole plant or its roots and leaves possess anthelmintic, diuretic, cardiac stimulant, diaphoretic, emetic, expectorant, febrifuge, laxative, anti-inflammatory and aphrodisiac properties. The herb can be used in all cases of inflammations. It is also effective against strangury, leucorrhea, opthalmia, myalgia and scabies. The extract helps prevent dyspepsia, constipation, cough, bronchitis, jaundice, cardiac problems and anemia. The numerous studies on animals suggest that the herb has potent anti-proliferative effects on varieties of cancer cells also enabled to prevent their metastasis. The most effective component in this regard is Purnavarine / Lunamarine, which is a quinolone alkaloid. The compound also exhibits antiesterogenic, immunomodulatory and anti-amoebic property.
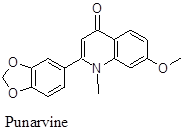
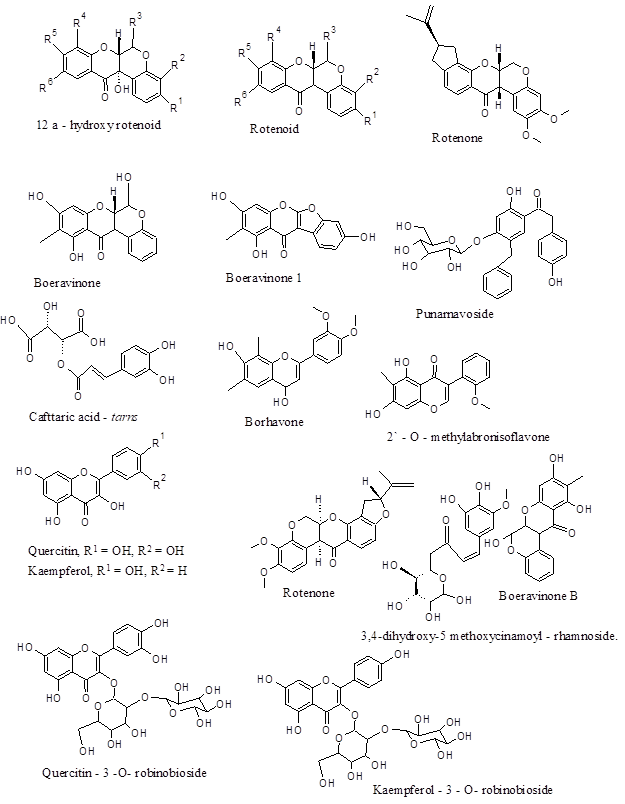
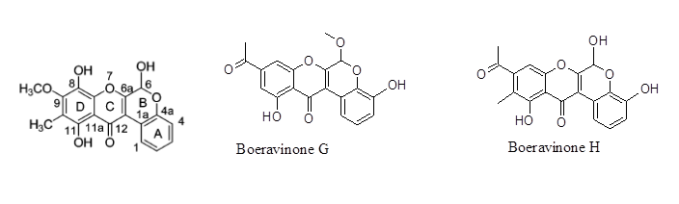
Chemical components: The herb is a good source of amino acids within roots and plant bodies. Additionally, BD has several fatty acids both saturated (38 %) and unsaturated (6.5 %). The plant contains few vitamins eg, C (45 mg), B3 (100 mg) and B2 (22 mg) (per 100 g). The level of Calcium is ~ 175 mg. The other important chemical components are β – sitosterol, Ursolic acid, stearic and palmitic acids, arachidic acid, boeravinone A to F, boerhavic acid, borhavine, campesterol, dauscosterol, ecdysone, flavones, and hypoxanthine. The plant synthesizes large reserve of flavonoids and isoflavonoids / rotenoids or rotenone. Rotenone inhibits mitochondrial electron transport property thus often used as pesticide or insecticides therefore toxic by nature. But the toxophore of Rotenone structure is phenyl derived ring and two – OCH3 substitution on the first phenyl ring. But those identified in BD are nontoxic because of the lacking of isoprenoid residue on D ring or having either unsubstituted or monosubstituted ring A. The major rotenoid in BD is boeravinone B which is ~ 0.005 %.
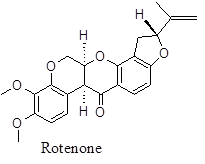
The rotenoids from BD show strong anticancer and antiinflammatory activities. Additionally, the triterpenes of BD eg, Ursolic acid, β – sitosterol and others also exert versatile beneficial effects on health. For example β – sitosterol is effective against benign hyperplasia also enables to reduce the blood pressure. Ursolic acid is a potent anticancer drug. Campesterol lowers LDL and cholesterol in plasma also precursor to several anabolic steroids. Ecdysone is a molting hormone mostly acts as antifeedant. It also has anti-hyperglycemic, immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective property. Below is the list of several chemical components and their physiologic effects. The compound, ecdysone also acts as anti-stress hormone.
Several important chemical constituents and effects of BD
| Types | Name of compound | Bioactivity | Plant part |
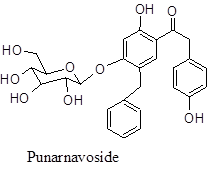
| Phenolic glycoside | Punarnavoside | Antifibrinolytic | Root |
| C- methyl flavone | Borhaavone | Root | |
| Isoflavone | 2`-O-methyl-abroisoflavone | ||
| Flavonoid | Quercitin, Kaempferol | Antioxidant | Leaves |
| Flavonoid glycoside | 3,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxy- cinnamoyl Rhamnoside, Quercitin-3-O-rhamanosyl (1-6)galactosides, Euplaitin 3 – O-galactosyl (1-2)glucoside, Kaempferol- 3- O- robinobioside, Eupalitin-3-O-β- Galactopyranoside. | Leaves | |
| Phenolic acid | Trans-caftaric acid | Roots. | |
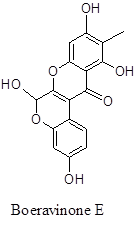
| Rotenoids | Boeravinones A, B, C, D, F | Roots | |
| Boeravinones G, H | Anticancer &
Spasmolytic |
Roots | |
| Boeravinones I, J | Roots | ||
| Boeravinones M, P, Q, R, S | Roots | ||
| Cocineones E, B | Roots | ||
| Diffusa rotenoid | Roots | ||
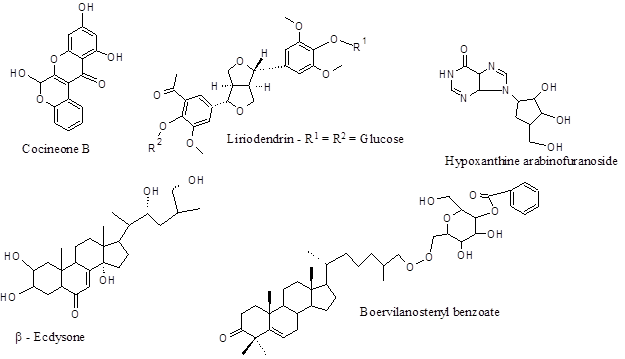
| Xanthone | Boerhavine | Roots | |
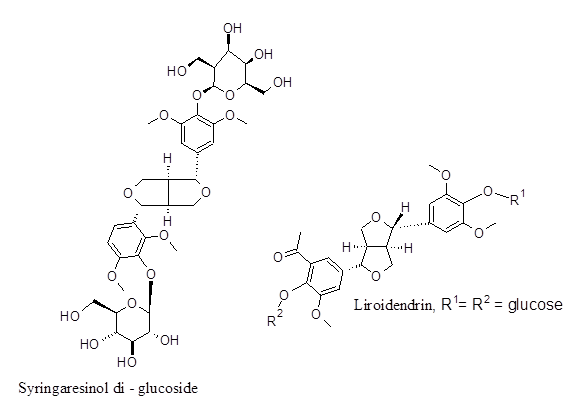
| Lignan | Liriodendrin | Ca+2 channel antagonist | Roots |
| Syringarsinol mono – β- glucoside | Ca+2 channel antagonist | Roots | |
| Purine nucleoside | Hypoxanthine-9-L-
arabinofuranoside |
Cardiotonic | Roots |
| Sterol | Boerhavisterol, β-sitosterol, campesterol | Roots | |
| Sterol ester | Boerhavilanostenyl benzoate | Roots | |
| Ecdysteroid | Β – ecdysone | Increase of protein
Synthesis, Antidepressant, Antistress, Immunomodulatory, Anti hyperglycemic, Hepatoprotective. |
Roots |
Chemical structure of several important chemical constituents of BD
Pharmacological effects: BD exhibits numerous pharmacological effects which have been already noticed from its versatile ethno-pharmacological usefulness. The majority of its uses are confined to kidney problems, jaundice, skin problems, healing wounds and inflammation, reproductive problems and eye diseases. Below are some of the facts verified from numerous laboratory experiments.
Anticancer effect – The ethanolic extract of root and leaf show cytotoxicity toward U – 87 MG (malignant glioma cell) and HeLa (cervical cancer) cell lines. Presumably, the major effect in this regard is exerted by the alkaloid fraction having Punarvine causing 40 % cell death. Further purification results in ~ 85 % cellular toxicity or cell death within 72 hours exposure when tested in vitro. It is noticed that Punarvine, the alkaloid isolated from BD can exert antibody dependent cellular and complement mediated cytotoxicity with enhancement of NK cell activity. The alkaloid also increases the production of IL – 2 and IFN – γ. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL- α, IL – 6 and TNF – α becomes considerably lowered by its administration. The compound can control lung melanoma possibly by downregulating the expression of MMP – 2, MMP – 9, VEGF, ERK – 1 and ERK – 2 in lung tissue. The extract is also effective in controlling other lymphoma and leukemic cells. Boeravinone G and H are identified to be strong efflux inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) belonging to the family of ATP binding cassette protein (ABCG2) which is often overexpressed in many cancer cells. BCRP tends to efflux varieties of anticancer drugs. Boeravinone G and H isolated from BD are seen to potently inhibit the efflux activity of BCRP. The isolation of other rotenoids and subsequent elucidation of chemical structures establishes the fact that there is a positive role of – OCH3 at 6 position of ring B also the absence of a substituent at position 10 also the necessity of 6a/12a double bond between B and C ring.
Antiinflammatory effect – Experiments regarding inflammatory models on laboratory rats show that the BD extract of leaf and flower can exert antiinflammatory effect by reducing ~ 56 % edema inflicted on rat paws. BD is famously known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions. The compounds Liroidendrin, syringaresinol diglucoside, quercitin and kaempferol could be responsible for the antiinflammatory and analgesic effects.
Hepatoprotective activity – In vivo studies using laboratory rats inflicted with several noxious stimuli like carbon tetrachloride or thioacetamide show significant protection or recovery in presence of BD root extract. The levels of SGPT, SAP, triglycerides and total lipid contents are lowered considerably. The histopathological view also supports the fact indicating trend to minimize the fatty cysts in the liver. The root extract by alcohol or aqueous media can provide protection also against paracetamol / Tylenol induced liver injury. The large presence of antioxidants within either extract is proven to be majorly responsible for this potent hepato-protective behavior. Besides present laboratory studies, the ethno-pharmacological reports have already proven that BD root extract is effective against numerous hepatotoxins.
Diuretic and renal activities – The administration of 0.5 – 1.0 % aqueous extract of BD is enable to dissolve and inhibit the struvite crystal growth (composed of Ammonium magnesium phosphate hexahydrate) within urinary canaliculi for women. The dissolution of crystals usually occur within 4 days by the use of 1% extract. Further the extract of aqueous or alcohol also produces significant diuresis. In animal studies on rats, the extract from roots enhances ~ 90 % urine volume whereas the same from leaf or flower causes ~ 63 % increase. Some suggest that the alkaloid, Punarvine and some level of choline components could be liable for this effect. Experiments have further shown that root extract prevents Calcium oxalate crystal formation, considered as kidney stone, urolithiasis. The serum ionic status and renal Na+ – K+ ATPase activity to increase diuresis could be the underlying reason behind the event.
Antidiabetic and hypoglycemic property – The BD leaf extract (200 mg / Kg) increases plasma insulin level (~ 10.4 µU / ml) which is comparable to 600 µg / Kg of Glibenclamide (~ 9.7 µU / ml). The chloroform extract of leaf can induce hypoglycemia dose-dependently. No specific component(s) has been identified yet.
Antioxidant effect – In vitro studies indicate that BD extract plays a large antioxidant role which could be related to its antiinflammatory, anti-Parkinson and anti- Alzheimer property. The extract has powerful ROS scavenging ability when tested against various free radical generating agents.
Anticonvulsant effect – The extract of BD shows potent anticonvulsant effect when tested on Pentylenetetrazole or Bay-k-8644 induced seizures in mice. The calcium antagonist property of extract is seemingly responsible for this effect. The compound liodendrin is possibly thought to exert the anticonvulsant activity.
Spasmolytic property – The introduction of methanolic extract of BD root on electrically or acetylcholine or histamine or BaCl2 stimulated isolated rat ileum shows significant spasmolytic actions (IC50 ~ 182 to 158 µg / ml of dried content). The effect occurs due to the involvement of extracellular Ca+2 ion but not the intracellular. The identified compound is Boeravinone E which is a powerful spasmolytic compound in the extract. Usually, the non-prenylated rotenoids are also the effective spasmolytic agents.
Antifungal and antimicrobial actions – The ethanolic and aqueous extract of whole plant shows powerful antimicrobial effect against number of bacteria. The minimum inhibitory concentration is 125 – 150 µg / ml. It works on both Gram positive and negative types. Its antifungal activity is noticed for ethylacetate extract for various fungi inhibiting 79 – 43 % in most of the cases. The alcoholic extract is also effective against tuberculosis, cough, diarrhea, eczema dysentry and urinary tract infections.
Antifibrinolytic action – The root extract of BD shows potent antifibrinolytic activity which is comparable to the usual agents like ε- aminocaproic acid, transexamic acid, naproxen and ibuprofen. The mechanism of action relates to NAD-dependent-15-hydroxy-prostaglandin dehydrogenase activity within the tissue. In that regard BD root is endorsed universally for many gynecological disorders like pain in female genital, regulation of menstruation, irregular high bleeding especially due to IUD insertion inside the uterus. Several phenolic glycoside, particularly Punarnavoside could be the underlying reason behind this effect.
Conclusion: The herb contains versatile chemical constituents that have diverse therapeutic effects offering hepatoprotection, diuresis, antitumor, antiinflammatory and several others. In addition the large reserve of rotenoids and its subsequent beneficial role on different types of diseases might help construct more efficient synthetic mimics to prevent or cure any ailments.
