Cordia dichotoma / Indian cherry / Clammy cherry / Gunda /শেলুকা / বুহাল / বহুবারা।

General features: The plant grows in moist tropical or subtropical regions of South and South East Asia, Papua New Guinea, Australia and other temperate zones which causes size variations concerning the plants, fruits and leaves. The botanical name is Cordia dichotoma (C dichotoma) but in English it is called Clammy cherry or Indian cherry. In Hindi it is named ‘Gunda’ whereas in Bengali it bears several names like ‘শেলুকা / বুহাল / বহুবারা।‘. The plant belongs to Borganaceae family. It is a deciduous tree which usually grows 10 – 16 ft tall and 4 – 5 ft wide. Some of the species can even grow further attaining ~ 70 ft high and 10 – 15 ft diameter bole. The stem bark is quite smooth and greyish brown. The unripe fruits are globular in shape, about 0.5 inch diameter with shining green or pinkish yellow that turns black on ripening. The flowers are short trailed, bisexual by nature and white in color that blooms at night. Flowering takes place from March and lasts until May when new leaves appear. Whereas the fruits ripen within June to August. The leaves are elliptical – lanceolate to broad ovate with round base which are also slightly dentate. The plant is considered being the native of Indian subcontinent, Indochina, Myanmar, Malaysia, Australia and Japan. In India it grows almost everywhere even in the dry climate of Rajasthan. The green fruits are pickled and frequently eaten with salads or with Chapatis as vegetable. The leaves are normally fed to the cattle. The tree as a whole has huge medicinal benefits. In rural India it is frequently used for anti-bacterial, anti-viral and antitussive uses. The folk uses of fruits are directed to treat common cold, fever, dyspepsia, cough, respiratory distress and catarrh. The stem bark can cure diarrhea, leprosy, gonorrhea and burning sensation during urination. Additionally, it also has numerous other medicinal and nutritional effects. About 300 species exist within the Cordia genus. Interestingly, all of them exhibit biological or physiological effects. Some even displays antifungal, larvicidal and anti-bacterial actions in addition to other health benefits preventing or curing various diseases and disorders. In Rajasthan and Western Ghats, the fresh flowers smashed in plain yogurts are often spread over the body for protecting against drastic heat and sun.
Nutritional and other aspects: The unripe green fruits are usually used for making pickle while preserving in spiced oil and lemon juice which is often eaten with salad or any cooked vegetables and Chapattis, the practice is popular in Indian dinner. In most occasions the ripen fruits are consumed to enjoy its sweet and astringent taste. The fruits have therapeutic values against diabetes especially owing to its Chromium content (0.2 mg / 100 g). The grinded seeds enriched with oils and proteins are consumed for the cattle food. The gum exuded from C dichotoma containing 97 % polysaccharide is used for the pharmaceutical needs. The plant also produces natural cellulose that can be woven for making the fabrics. Table shows the nutritional content of leaves, seeds and fruits.
| Plant part | Nutritional component ( / 100 g) |
| Leaves | 15 % protein, 27 % crude fibers, 52 % Nitrogen free extract, ~17 % Ash, 4 % Ca, 0.3 % Phosphorous. |
| Seeds | 32 g water, 46 % oil, 31 % protein. |
| Fruits | 6 g water, 35 g protein, 37 g fat, 18 g carbohydrate, Ca – 55mg, P – 275 mg, Zn – 2mg, Fe – 6mg, Mn – 2mg, Cr – 0.2 mg, Cu – 1.6 mg. |
Folk medicinal use: The plant has been known for ages due its large potential to treat numerous health problems which has been already introduced in the Ayurveda. It is also included in the Mediterranean Unani medicine of Persian and Arabic nations. The bark extract is commonly used to treat dyspepsia. Often it is mixed with pomegranate to control the dysentry. But to minimize the colic pain the extract is often mixed with coconut water. The leaves, fruits, bark and seeds exhibit anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and immune modulating properties. The fruit extract or syrup made from it are used to treat following health problems: 1) Fever, 2) Cough, 3) Worm infestations, 4) Blood & bleeding disorders, 5) Seminal problems (untimely or less ejaculation volume) and 6) Asthma. The fruits are heavily enriched with medicinal components. Like fruits, the bark extract is used for treating; 1) Blood disorders, 2) Wounds, 3) Digestive help, 4) Small pox, 5) colic due to intestinal worms, 6) Leprosy, 7) spider bite, 8) Blisters and 9) ulcers. In Mediterranean regions like in Egypt, dried fruits are sold in the market as Sapistan which are used as Unani medicine. The dried fruits have effects on chronic bronchitis, influenza and also acts as laxative.
Chemical components: The major phyto-components identified in leaves, fruits, seeds and barks fall into the categories of pyrrolizidine alkaloids, coumarins, flavonoids, saponins, terpenes and sterols.
Seeds – Betulin, α – amyrin, octasanol, Lupeol – 3-rhamnoside, β – sitosterol, β – sitosterol – 3 – glucoside, hentricontanol, hentriacontane, taxifolin – 3 – 5-di-rhamnoside, hespiritin – 7 – Rhamnoside and fatty acids (palmitic, stearic, arachidic, behenic, oleic, linoleic acid). Few flavonoid glycosides (robinin, rutin, rutoside, datiscoside and hesperidin) and a flavonoid glycone (dihydro-robinatin) and 2 phenolic derivatives (chlorogenic and Caffeic acids).
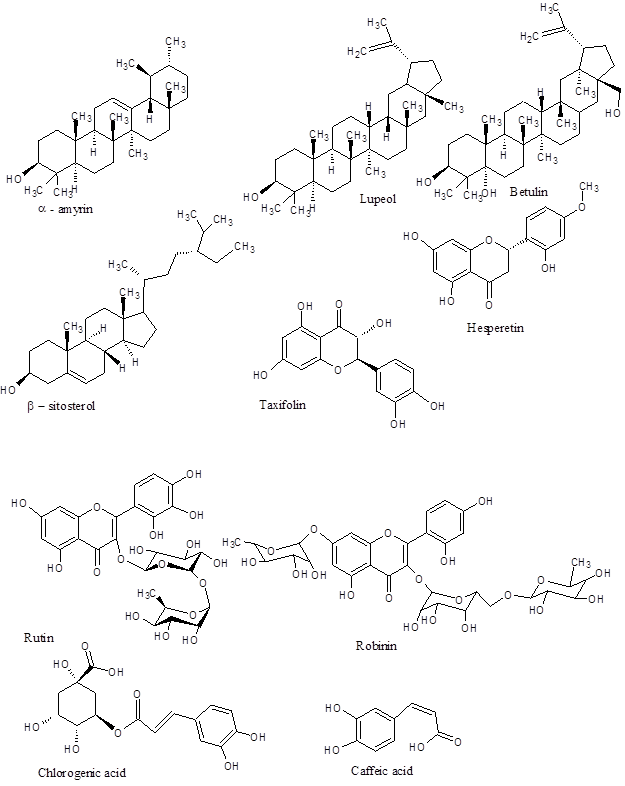
Major chemical components from seeds
Bark – Allantoin, β – sitosterol, 3`- 5-di-hydroxy-4`-methoxy flavanone – 7 – O – α – rhamnopyranoside and gallic acid.
Fruits & leaves – Pyrrolizidine alkaloids like Macrophylline, coumarins, flavonoids, terpenes and sterols like β – sitosterol. Further fruits also produce arabino-glucan, D- glucose and L-arabinose. They also contain quercetin and quercitrin.
A large majorities of the similar compounds have been usually identified throughout the plant.
Pharmacological properties: The pharmacological role of extracts of plant parts are studied in the laboratory and some of the corresponding active components are subsequently identified. For example, the ethanolic extract of bark shows significant antibacterial and antifungal actions. It is active against Gram negative bacteria like E coli, P aeruginosa and Staph aureus. The antifungal effect is studied and confirmed against Aspergillus Niger, Aspergillus clavatus and Candida albicans, the pathogenic fungi. The antibacterial effect is comparable to ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and chloramphenicol whereas the antifungal action is closely similar to Nystatin and Griseofulvin. Recent discoveries indicate that naturally occurring flavonoids could be immensely responsible for the antibacterial and antifungal actions. The mechanism behind the effects are due to several reasons, inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis, cytoplasmic membrane function, energy metabolism, preventing biofilm formation, inhibiting porin action on cell membrane, altering membrane permeability and reducing the pathogenicity. The other important component in bark extract is Allantoin which is often used in the cosmetics for moisturizing and keratolytic effect. It also has medicinal effects in producing wound healing, exerting soothing effect and anti-irritant effect. It is a good skin protectant also acts an inflammatory modulator. Allantoin helps fibroblast proliferation and often used as desquamation of upper dead skin layers. In case of atopic dermatitis, instead of steroids, Allantoin is applied also. The presence of β – sitosterol in appreciable level makes the extract medicinally important. The compound exhibits enormous physiological role acting against allergies, inflammation, asthma, bronchitis, and rheumatic arthritis, also lowering plasma cholesterol preventing heart diseases, prostate and colon cancers, benign prostate hyperplasia and relieving pain, boosting immune system and enhancing sexual function. The extract of fruits and leaves have strong antioxidant role due to the presence of flavonoids, saponins, coumarins and others. But the potent antimicrobial properties is noticed in leaf extract due to the presence of Macrophylline which is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid.

Concerning coumarin and its derivatives, they have enormous medicinal uses. It is usually used as anti-coagulant (Warfarin) and increasing the level of anti-thrombin in plasma also used for treating lymphedema. The compounds exerts uricosuric (helping removing urea from circulation) and antioxidant effect. Coumarins has potent antimicrobial role too. The triterpene Betulin shows strong anti-tumor activity. It enhances insulin sensitivity, lowers obesity, atherosclerosis, lymphatic diseases and tuberculosis and several other health problems. Amyrin has anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects via the activation of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) also inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines like NF – κβ, COX – 2 and CREB (transcription factor for cAMP binding element). Lupeol is a pentacyclic triterpene, sterol by the nature. Like the others it also exerts considerable physiologic effects. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-protozoal, anti-proliferative, anti-invasive, anti-angiogenic and cholesterol reducing agent. Studies indicate that Lupeol modulates IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL – β, proteases, cFLIP, Bcl-2 and NF-κβ. Taxifolin and its glycosides are potent anti-oxidant also having significant anti-tumor effects on ovarian cancers by inhibiting fatty acid synthase enzymes. It is also useful against methicillin resistant staphylococcus bacteria. The high level of flavonoids and its various glycosides makes this plant very healthy for diet. Besides being anti-oxidant, they are good for cardio-vascular diseases, exert anti-cancer effect, being anti-inflammatory and often anti-bacterial also. The phenolic derivatives like Caffeic acid or Chlorogenic acid have numerous biological effects. For example, Caffeic and Chlorogenic acids have strong anti-oxidant actions and also exhibits anti-inflammatory effect. In addition they can slightly lower the arterial pressure. Caffeic acid on the other hand has immunomodulatory effect and in addition it shows anti-tumor role particularly Fibrosarcoma when studied in vitro using human HT – 1080 cell line.
Medicinal uses: The majority of medicinal uses are followed by viewing the folk practices. The tasty fruits are edible and seen to be effective against colic pain, cough, fever and several diseases of skin also for seminal weakness or sexual disorders. The bark extract is effective against many illnesses due to its large content of Gallic acid and β – sitosterol.
Bark – The extract is used as tonic to prevent colic, dysentery, dyspepsia, chronic diarrhea, strangury and catarrh. It is further used in controlling fever, boil and tumor, and also ulcers in the mouth. Gargling the extract can even strengthen the teeth. It provides relief on itch. Both bark and root extract has strong larvicidal property in addition to fungicidal and destroying several pathogenic parasites due to the presence of meroterpenoid napthaquinones and cordioquinones.
Seeds – The seed extract has potent free radical scavenging property owning to the presence of abundant level of flavonoids like Kaempferol, Quercitin, iso-rhamnetin and Taxifolin. In addition the extract also exhibit strong anti-inflammatory action. The methanolic extract has powerful anti-microbial, anti-fungal and larvicidal effects.

Fruits – The fruits or its extract or mucilage can treat coughs, problems of chest, uterus urethra also acts as laxative. The ripe fruits are sweet and demulscent.
Kernel of fruits – This extract can cure ringworm when applied on the specific areas.
Leaf – The alcoholic extract leaf shows abortifacient effect on female laboratory rats also indicate anti-implantation action thus acting as natural contraceptive. But they are effective in reducing headache and ulcers.

