Eclipta Alba / Eclipta Prostrata / Bhringaraj / ভৃঙ্গরাজ

General features: The plant grows in moist tropical climate, commonly known as False-daisy, Yerba de Togo, Kehraj or Karisalankanni. In India it has been used as Ayurvedic medicine to cure or prevent various ailments for few millennia. The herb belongs to Asteraceae (sunflower) family that grows across the world but majorly noticed in India, Nepal, Southern China, Thailand, Vietnam and several tropical regions of South American countries like Brazil, Peru and others. It is also occasionally found in the many wildernesses of North American nations like US and Mexico. The reddish-purple stem of the plant is about 36 inches tall and appears cylindrical having grayish roots producing white flowerheads, 0.25 – 0.32inch diameter whose achenes are compressed and headed. The leaves are ovate or egg-shaped. In most places of the India it is ordinarily named as Bhringaraj (ভৃঙ্গরাজ). It is also botanically called Wedelia Calendulacea which often grows two kinds displaying white and yellow colored flowers. Both have almost the similar ingredients producing identical health impacts. The plant has been traditionally used as Ayurvedic medicine also recognized as being popular for its number of medicinal role either to cure or prevent various common ailments like liver problems, diabetes, hair growth, eye health etc. The extract of Eclipta Alba is known for a long time to be effective in hair-growth (topical application of Pet-ether extract – 5%) and experimentally claimed as being comparable to 2 % solution of Minoxidil (anti-hypertensive medication often used to cure hair loss particularly for the androgenic alopecia). For oral intake, either ethanolic extract or else the fresh plants is used as vegetable. It has pain reduction abilities outperforming Aspirin. It even receives attention for blood pressure lowering ability, anger management, diuretic action and immune boosting effects. Its further use is now seen in varieties of cosmetics and beauty products claiming to have a promising role on skin tone. It is a good mosquito repellant also displaying anti-venom and anti-viral properties. In many parts of India especially in North and South regions, the leaves of E. Alba are often consumed as vegetable eating with lentil soup along with the other vegetables and rice.
Bhringaraj oil for hair growth and regeneration: From the very ancient time the extract from its leaves is used either to regenerate or grow or even removal of gray coloration from the hair. In recent days, number of animal experiments have established the effects and some of the components are also identified, although not exactly. The components stimulate blood circulation of the scalp and help secreting few factors enabling to rejuvenate the hair follicles for hair growth. Many people prepare this herbal oil at home using fresh leaves of E. Alba. In most occasion refined coconut or olive oil is used for the extraction while heating with chopped or paste prepared from the leaves. After filtering the concoction through nylon mesh, the oil extract is stored in a bottle. Before its use, the oil is slightly warmed up and massaged on the scalp for quick absorption. The effect can be observed in ~ 2 month period.
Phytochemicals produced in different parts of the plant:
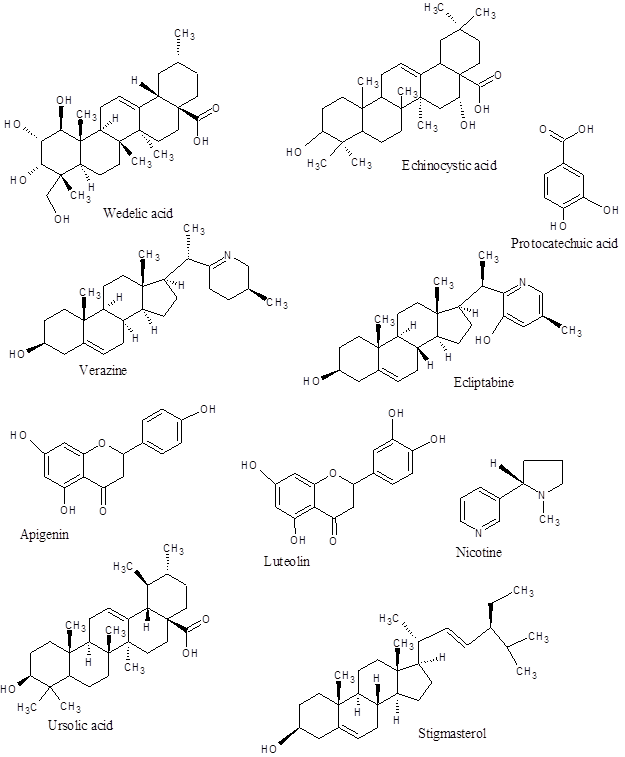
Leaves – Coumestan derivatives like Wedelolactone, Des-methyl-Wedelolactone, Stigmasterol, α – terthienyl methanol, Des-methyl-Wedelolactone – 7-glucoside, Alkaloids, Apigenin, Luteolin, Wedelic acid, 25 – β – hydroxy-Verazine, Ecliptine and Nicotine.
Roots – thiophene, eg, 5I-senecioyl-oxymethylene-2-(4-isovaleryl-oxybut-3-ynyl)-dithiphene and several of its identical derivatives, 1-Hetriacontanol (straight chain alcohol C31 H63 OH), Stigmasterol, Ecliptal and 14-heptacosanol.
Stems – Wedelolactone, Wedelic acid, L-terthienyl methanol, Apigenin and Luteolin.
Seeds – large reserve of various sterols. Wedelic acid and Echinocystic acid are triterpene. They can be found also in glycoside forms.
Aerial parts – β – amyrin, Luteolin, Luteolin – 7 – O glucoside, Apigenin, Wedelolactone, Thiophene derivatives and Eclaba saponins.
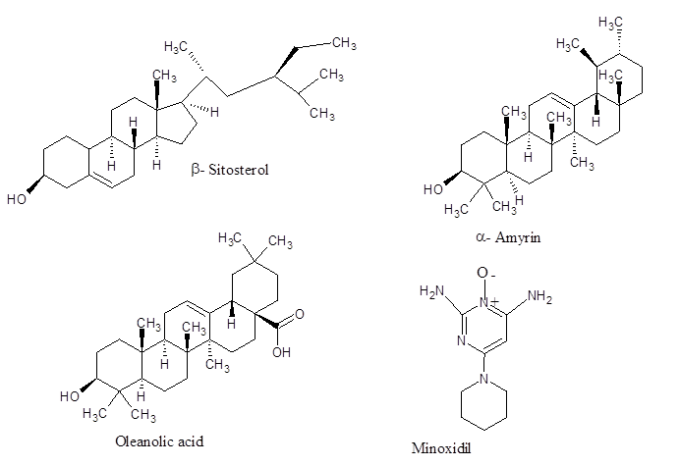
Whole plant – Ecliptine, Sugars, Resin, Nicotine, Stigmasterol, Tri-terpene saponins, Eclalbatin, Ursolic acid and Oleanolic acid.
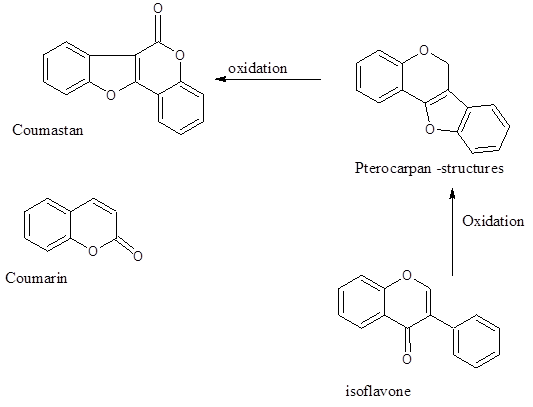
Major chemical components and its properties: It has been noticed that the herb produces a great many number of bioactive compounds which comprises Wedelolactone, Des-methyl-Wedelolactone, triterpenes, flavonoids, steroids, polypeptides, poly-acetylenes and thiophene derivatives. The extract offers numerous pharmacological properties eg, antimicrobial, analgesic, anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, anticancer and others. Additionally a large section of terpenoids along with their respective glycosylated derivatives are isolated as well as characterized for bioactivities. Few physiologically active alkaloids are identified also in this herb. The root extract contains poly-acetylene and thiophene compounds. In several occasions, the extract also shows the presence of Nicotine and Nicotinic acid along with Verazine, Ecliptabine and few other alkaloids. Besides those components, there are number of Coumestan analogs like Wedelolactone, Des-methyl – Wedelolactone but not the Wedelic acid which is a triterpene also available in the plant. The Coumestans are generated by the enzymatic oxidation of Pterocarpan which is also produced via the oxidation of isoflavone. Coumestans are very similar to the bioactive compound, Coumarin (normally used in treating lymph-edema also enhances plasma Anti-thrombin III preventing arterial blood clotting). Coumestrol binds to the ER- β – estrogen receptor mimicking 17 β – estradiol with lesser affinity than 17 α – estradiol. In that way it acts as a phyto-estrogen.
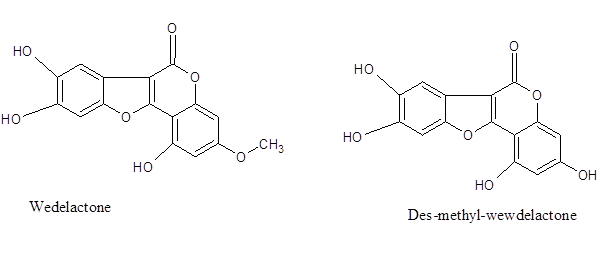
The Coumestans and its analogs like Wedelolactone or Des-methyl-Wedelolactone are best extracted (~ 16 %) by the ethylacetate whereas alcoholic extraction provides much less (~ 4 %). Wedelolactone analogues are probably the most bioactive products.
The role of Wedelolactone and its analogues like Coumestans are enormous. Below is some of their effects and way of actions.
Anti-inflammatory effect – It suppresses production of IL-6, TNF – α and subsequent PGE2 generation. In addition, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-asthmatic manifestations of Wedelolactone and Gallic acid occur via the interaction with G-protein coupled receptor – 35 (orphan receptor) while behaving as agonists. The effect is somewhat identical to Cromolyn (di-sodium – chromoglycate), a potent anti-asthmatic, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic drug.
Beneficial effect on osteoporosis – The compound enhances osteoblastogenesis via ER, JNK mediated BMP-2 and smad1/5/8 phosphorylation.
Anti-cancer role – It can inhibit estrogen receptor mediated breast, endometrial and ovarian cell growth. It also downregulates c-Myc oncogene in most of the prostate cancer cells. It also prevents abnormal proliferation by regulating key members of NF – κβ signaling pathway.
Miscellaneous effects – The compound inhibits Na+/K+ – ATPase in kidney tubule thus producing significant effect on the arterial blood pressure. Further it also interacts with the Benzodiazepine receptor in CNS thereby acting as an anxiolytic drug producing calming effect along with induction of sleep in brain. Ecliptal / Des-methyl-Wedelolactone besides acting as Na+/K+ – ATPase inhibitor also inhibits other enzymes like DNA helicase-1 (used during DNA, RNA strand separation) and Tyrosine – DNA-phosphodiesterase polymerase kappa (inhibiting NF – κβ generation). Both of the compound can inhibit trypsin. It is the underlying reason behind appetite reducing effect of this herb.
Analgesic effect – The effect has been confirmed by animal experiments using all the models. The alkaloid fraction of ethanolic extract has been identified to be the most efficient in this aspect.
Anti-inflammatory effect – The oral administration of alcoholic extract showed dose-dependent anti-inflammatory action in the experiments using various animal models. The effect is possibly due to Wedelolactone and other related derivatives inhibiting the action of 5- lipoxygenase.
Anti-aggressive behavior – The anti-aggressive and calming behavior has proven by the animal experiments using aqueous extract of E. Alba. The effect is dose-dependent, 100 – 200 mg / Kg. No exact chemical components have been identified but preliminary works indicate that Apigenin and several others could be responsible behind that act.
Anti-bacterial, Anti-fungal & Anti-malarial actions – The effective component(s) is Wedelolactone and its other derivatives. The extract is tested against bacterial species like Staphylococcus epidermis, Salmonella typhimurium and several others. It shows good potency at 25 µg / ml. The extract or Wedelolactone fractions are superbly active against many fungi eg, Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis and Rhodotorula glutinis. The effects are much comparable to the standard antibiotics used against respective fungi. The anti-malarial actions are tested in animal model using ANKA strain mice infected with Plasmodium berghei. The leaf extract shows schizontocidal effect (destruction of sporozoan parasite) to suppress the infection.
Anti-hyperglycemic effect – If taken orally (leaf suspension 2 – 4 gm / Kg body weight) for about two months then it would significantly lower the blood glucose level (from 372 ± 33 to 117 ± 23) including the reduction of HbA1C. A subsequent decrease of glucose – 6 – phosphatase and fructose 1, 6 bisphosphatase along with the increase of activity of liver hexokinase has been observed.
Hepato-protective effect – Using animal experiments it has been proved that E Alba extract provides potent hepatoprotective action against CCl4 injury or Tylenol induced toxicity of the liver. One of the identifiable components is Oleanolic acid.
Hypolipidemic effect – The alcoholic extract causes significant reduction when assessed by the lipid profile of serum and liver. The triglyceride, total cholesterol as well as low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are also reduced to the considerable extent. A number of components are responsible for the effect.
Neuropharmacological effect – Experiments on animals convinced that consumption of aqueous or alcoholic extract enhances learning and cognitive behavior. The daily use of this herb shows strong nootropic effect, particularly for the human. Combination of several identifiable factors are responsible for the effect.
